National Immunization Awareness Month (NIAM) is observed in the month of August to highlight the importance of immunizations for people of all ages, from infants to the elderly. The observance is organized by various health organizations, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), to highlight the benefits of vaccinations and encourage individuals to stay up-to-date with their immunizations.
During National Immunization Awareness Month, public health campaigns and initiatives are launched to promote the following key messages:
- The importance of vaccination. The primary focus is to emphasize the role of vaccines in preventing serious and sometimes life-threatening diseases.
- Vaccine safety. The campaigns aim to address concerns and misconceptions about vaccine safety by providing accurate and evidence-based information.
- Immunization schedules. Information about recommended immunization schedules for different age groups, including children, adolescents, adults and seniors, is shared to help individuals and families stay on track with their vaccinations.
- Disease prevention. By showcasing success stories of diseases that have been controlled or eradicated through immunization efforts, NIAM highlights the positive impact of vaccines on public health.
- Accessibility. The campaigns may also address barriers to immunization, such as lack of access to healthcare services, and provide information about available resources.

Why is the observance important?
During National Immunization Awareness Month, healthcare providers, schools, community organizations, and media outlets often collaborate to spread accurate information about vaccines and their importance. These efforts are intended to help individuals and families make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Several diseases that can be more prevalent during the summer months can be prevented or mitigated through vaccinations. Here are some examples:
- Influenza (Flu): While influenza is more commonly associated with the colder months, there are strains of the flu virus that circulate year-round, including during the summer. Annual flu vaccines are recommended to protect against the most prevalent strains of the virus. Getting vaccinated can help reduce the risk of severe illness and complications from the flu.
- Measles: Measles is a highly contagious viral infection that can lead to serious complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis. Travel and increased gatherings during the summer can facilitate the spread of measles. Ensuring that individuals are up-to-date with their measles vaccinations is important in preventing outbreaks.
- Mumps: Mumps is another contagious viral infection that can spread easily in crowded settings. Like measles, mumps can cause complications such as swelling of the salivary glands, fever and discomfort. The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine provides protection against mumps.
- Chickenpox (Varicella): Chickenpox is often associated with childhood, but it can affect people of all ages. Summer can be a time when chickenpox spreads, as people spend more time outdoors and in close contact with others. Immunization with the varicella vaccine can help prevent chickenpox.
- Meningococcal Disease: Meningococcal disease, including meningitis, can occur more frequently during summer camps, college orientations and other gatherings where people are in close quarters. Meningococcal vaccines are available to protect against different strains of the bacteria that cause these diseases.
- Travel-Related Diseases: Many people travel during the summer and -- depending on the destination -- they might be at risk for diseases not commonly found in their home country. Vaccines such as those for typhoid, hepatitis A, and yellow fever might be recommended for travelers to certain areas.
- Tick-Borne Diseases: A vaccine for tick-borne diseases like tick-borne encephalitis was approved by the CDC. This can be important for travelers visiting Asia or Europe, where it is prevalent.

What can pharmacists do to support NIAM?
Pharmacists play a crucial role in supporting National Immunization Awareness Month by actively promoting the importance of vaccinations and helping individuals stay up-to-date on their immunizations. Here are several ways pharmacists can contribute:
- Education and Counseling: Pharmacists can provide accurate and up-to-date information about vaccines, addressing any concerns or misconceptions patients may have. They can explain the benefits of vaccination, the recommended schedules for different age groups, and the protection vaccines offer against various diseases.
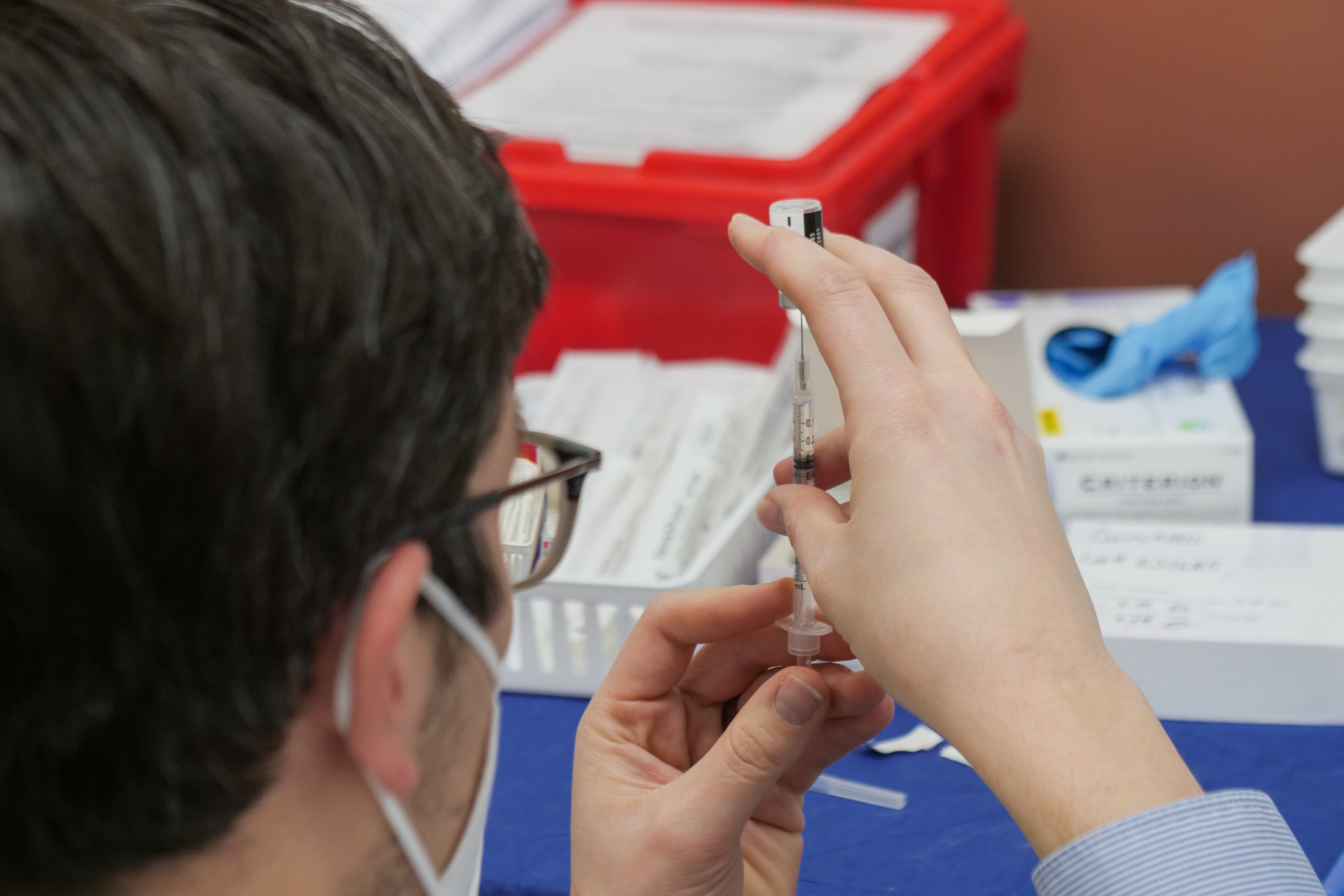
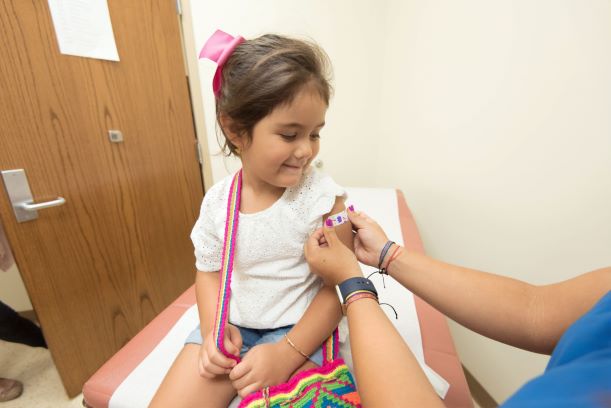
- Vaccination Clinics: Many pharmacies offer vaccination services, allowing individuals to receive vaccines on site. Pharmacists can organize and promote vaccination clinics specifically during National Immunization Awareness Month to encourage people to get vaccinated.
- Vaccine Administration: Pharmacists are trained to administer vaccines safely and effectively. They can administer vaccines based on recommended schedules for children, adolescents, adults and seniors. Administering vaccines, point-of-care testing, and other services can be a lucrative business for pharmacies. For a discussion on other Non-PBM revenue sources, read our related blog post here.
- Review and Recommendations: Pharmacists can review a patient's immunization history to identify any vaccines that are due or overdue. They can recommend appropriate vaccines based on a person's age, health conditions and risk factors.
- Promotional Activities: Pharmacists can collaborate with their pharmacy teams to create eye-catching displays, posters and informational materials about National Immunization Awareness Month. This helps raise awareness among patients who visit the pharmacy.
- Social Media and Online Engagement: Pharmacies can utilize social media platforms and their websites to share educational content about immunizations. This could include infographics, videos, articles, and frequently asked questions about vaccines.
- Community Outreach: Pharmacists can partner with local schools, community centers, and healthcare organizations to organize educational events, workshops, or seminars about the importance of vaccinations.
- Engaging Special Populations: Pharmacists can focus on reaching out to underserved or vulnerable populations who may have limited access to healthcare services. They can offer information about low-cost or free vaccination programs.
- Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy: Pharmacists are well-positioned to engage in conversations with individuals who might be hesitant about vaccines. They can provide evidence-based information to address concerns and encourage informed decision-making.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Pharmacists can collaborate with physicians, nurses and other healthcare providers to ensure coordinated and comprehensive care. This can involve sharing immunization records and discussing vaccination plans.
- Continuing Education: Pharmacists can stay updated on the latest vaccine recommendations and guidelines through continuing education opportunities. This ensures that they provide the most accurate and current information to their patients.
By actively participating in these activities, pharmacists can contribute significantly to raising awareness about the importance of immunizations, increasing vaccination rates, and ultimately improving public health within their communities.




.png)